Aggression Between Cats After a Vet Visit
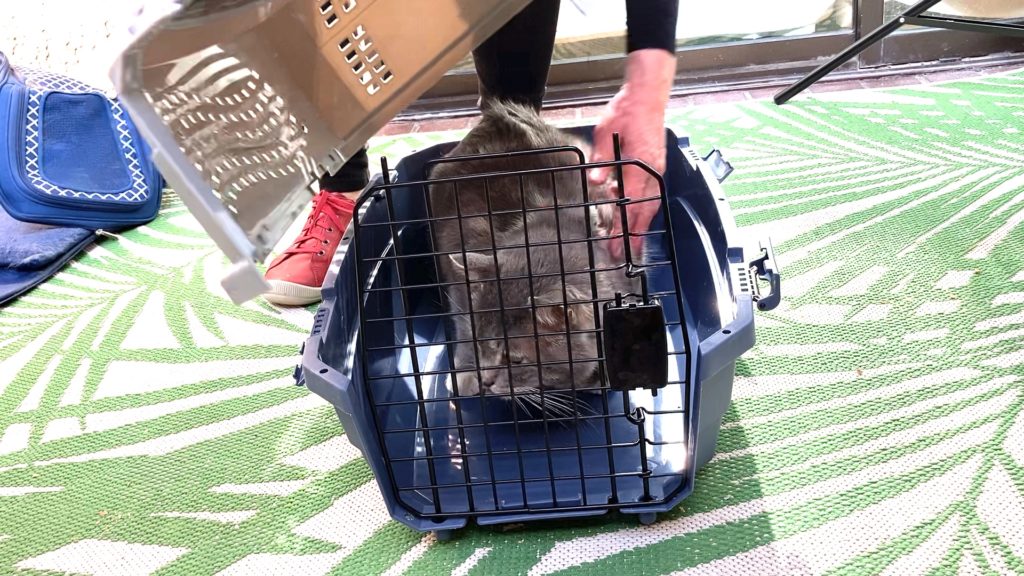
Zelda, my 5 year old Maine coon cat, went into the vet clinic on a Tuesday to have her teeth cleaned and to finish her lion cut that I started the day before. Zelda did well with anesthesia, teeth cleaning and lion cut. Upon returning home, Zelda stayed in the master bedroom for a few more hours for her anesthesia to wear off.
In the past, there has been some aggression between cats after one of the cats comes back from his or her veterinary visit. In particular, Gus, my former street cat, has been aggressive towards the other cats when they come home from the hospital. So, I made sure that the Feliway multi-cat pheromone diffuser was plugged in and bagged up the blanket Gus sleeps on for Zelda to use in her carrier on the way home.
In spite of all my precautions, Gus was agitated and aggressive not only with Zelda, but also with the older cats, Marley and Athena, when I let Zelda out of the bedroom for dinner. Not only did he strike at the other cats when they got too close, he went out of his way to strike at them if they were out of reach.

The aggression between cats continued into Wednesday and I found myself starting to lose my patience with Gus, who was the instigator. So time for some “tough love” – Gus was asked to go to his safe place. The door was closed and he spent the afternoon in the back office with some treats and his snuffle mat.
His attitude was much better when he was released at dinner time. The next morning, Thursday, Zelda greeted him with a quick lick that he was not overly enthused about but he accepted.
What is the take-away here?
The smell of the vet clinic is disturbing to Gus – he associates it with unpleasant experiences. I also think he finds it confusing and frightening when his housemates smell like the hospital – he is not sure who they really are and this makes him anxious and afraid.
The safe place smells familiar and is quiet. It conveys a feeling of calm and safety and this helped Gus change his emotional state. By the time dinner came around, Zelda’s “hospital” smell had faded a bit more and the dinner routine helped reassure Gus. He remained calm and did not go out of his way to swat the other cats.
Going to the safe place is not a like the time-out used with human children. The time-out spot for children is a spot with minimal stimulation and away from other people. The idea is to remove the child from whatever was reinforcing the undesired behavior and have him/her calm down, link his or her behavior to the wrongdoing, and change it.
Your cat will not link misbehavior with being isolated (human toddlers have trouble with this also). The safe place is not a punishment – it has all your cat’s resources (litter boxes and toys) and allows you to remove him from whatever is stimulating the “bad” behavior, in this case, the aggression between cats. The safe place should convey a feeling of calm to your cat and change his emotional state, from one of possible arousal and fear to one of calm and security. Once your cat feels calm and secure again, you will be able to interact with him and communicate with him – he should be able to respond to any training he has had. In this case, if reintroduction is not successful after some “quiet time”, you may need to try a more gradual reintroduction. See Introducing Cats: A Short Guide






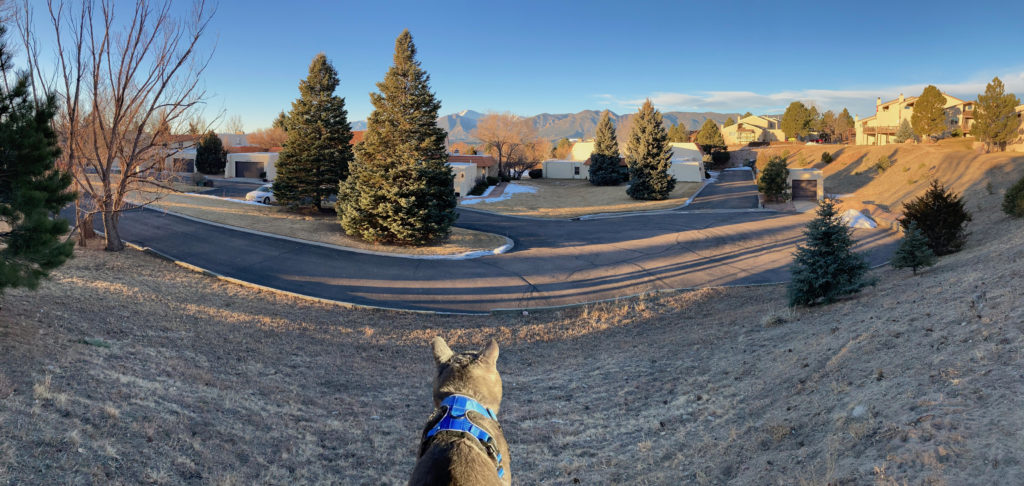
 I have seen a lot of advertisements and posts recently on social media about taking your cat for a walk. This can be a source of enrichment for your cat; it is also be a great time to take photos of your friend and bond with her more.
I have seen a lot of advertisements and posts recently on social media about taking your cat for a walk. This can be a source of enrichment for your cat; it is also be a great time to take photos of your friend and bond with her more.