Your cat’s carrier should be his castle. His carrier should be a place of safety and comfort, a little piece of home away from home. Cats are territorial and are attached to their territory. When your cat travels, the stroller, backpack or carrier is part of his territory – it has his scent and is a “safe place” for him.
You may need different carriers depending on what you are doing. Strollers and backpacks are more suited to walking or hiking with your cat. A kennel-style cat carrier is better for extended car travel and veterinary visits.
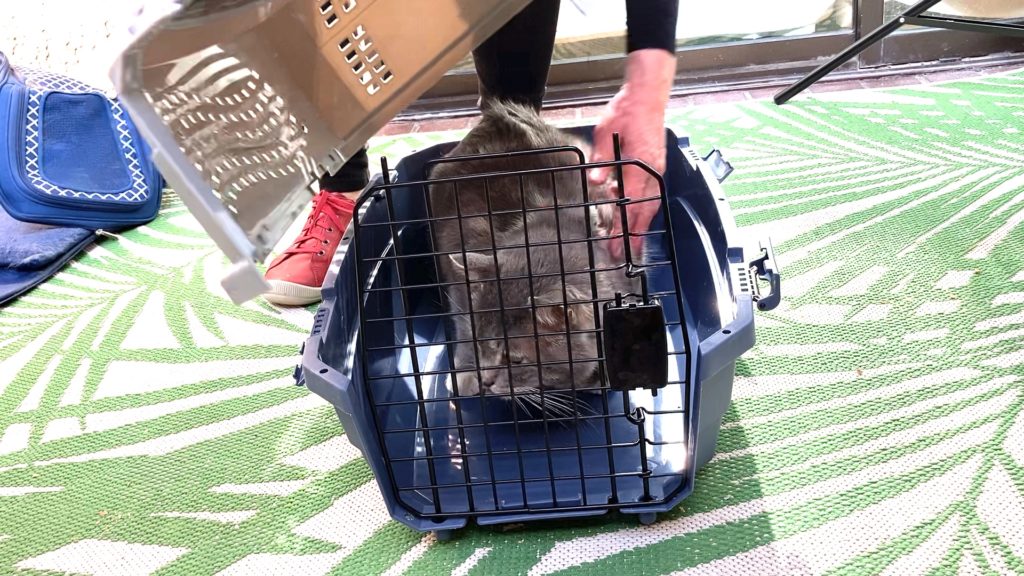

There are many kennel-style cat carriers that you can buy. Here are some tips when choosing a cat carrier that you plan to use for extended car travel or vet visits.
- the carrier should be large enough for your cat to stand up and turn around.
- it should have a rigid frame so that it does not collapse on your cat.
- it should be easy to take apart or have more than one opening where you can easily remove your cat from the carrier
- easy to clean
- make your cat feel safe and secure – like a wildcat’s den
Tips for Choosing a Cat Carrier for Car Travel and Vet Visits…
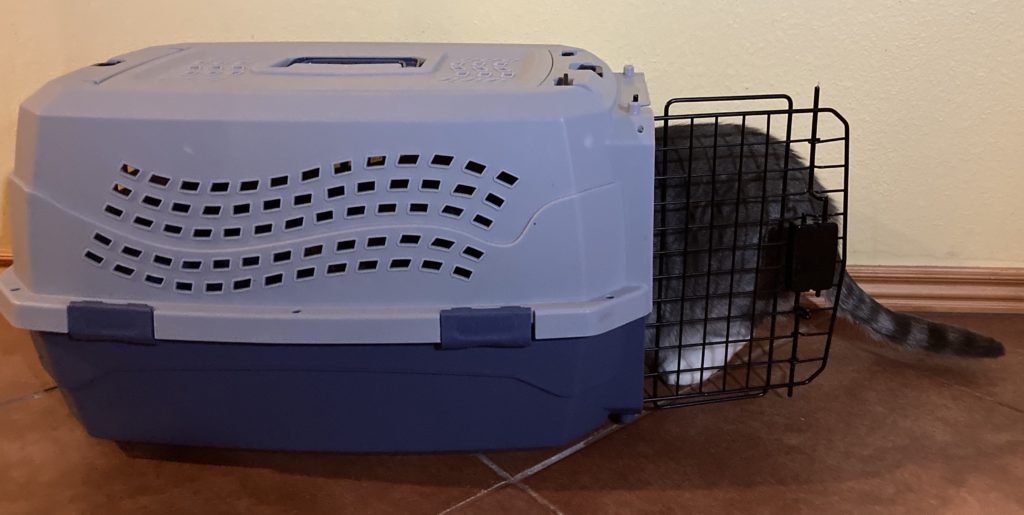
Hard, plastic carriers
- come in lots of sizes.
- many have detachable tops which makes getting your cat in and out easy
- they are easy to clean
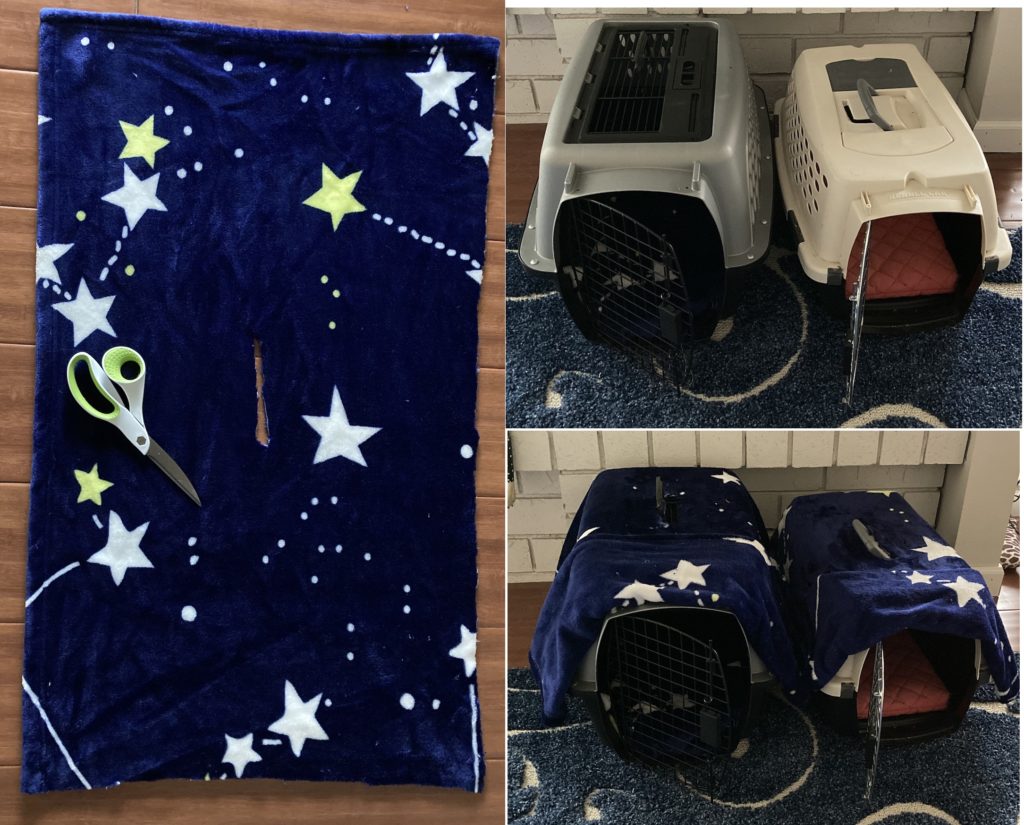
- can be covered with a blanket or towel to make your cat feel secure
Flexible, fabric carriers
- attractive and are not as bulky as the hard plastic ones
- some of these carriers tend to collapse in on your cat and are not as comfortable for him to stay in for longer periods of time
- more difficult to clean than the hard, plastic kennels
Even if the carrier is rigid and has a top panel that zips open or unlatches, it can be difficult to put the cat in when he doesn’t volunteer to go in on his own. It can be hard to fit your cat and your hands through the top panels. Some fabric carriers have a zippered front and side mesh panels, making loading and unloading a bit easier.
Choosing a cat carrier that comes apart into two sections – a top and a bottom – can be really handy. If you need to get the cat out of the carrier, you can remove the top half and gently pick him up out of the bottom. You can put him back in the carrier in the same way. Your veterinarian can examine your cat in the bottom half of the carrier, where he feels safe. The bottom half can double as a basket to sleep in.
Choosing a Cat Carrier…Make your Cat’s Carrier His Castle
THERE’S NO PLACE LIKE HOME
Leave the carrier out at home and let your cat nap and play in it. Place it in a “neutral” area – away from food and litter boxes.
PURRSONALIZE THE CARRIER
Place a towel or blanket that has your cat’s smell in the carrier. Put some of his favorite toys and treats in the carrier.
FUN AND GAMES
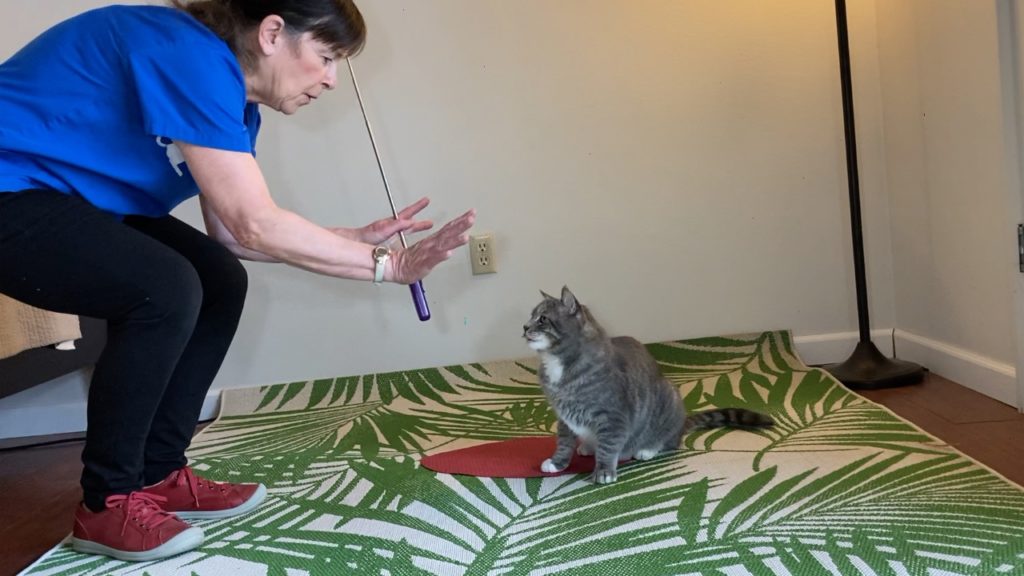
You can also play games with your cat in and around the carrier. If your cat is fond of “treat toss” (tossing treats that kitty “hunts” down), make sure some treats go into the carrier during the game.
TAKE KITTY FOR CAR RIDES THAT DON’T END UP AT THE VET.
Start with short rides, maybe just around the block. Work up to longer rides to pleasant places – if you have a cat stroller you could work up to going for walks in the park. Remember, always move at your cat’s pace – if he is hunched and hiding, slow down and shorten the length of the ride until kitty is comfortable. Ask your vet about treating carsickness if your cat is prone to it.
CLEAN AS A WHISTLE
Clean your cat’s carrier regularly. When you are finished, spray the carrier and the bedding inside with Feliway, a synthetic feline pheromone that tells your cat that this a safe place. Make sure to give enough time for the alcohol in the spray to dissipate before using the carrier – 20 minutes should do the trick!

Car travel – where to put your cat’s carrier in the car
The Center for Pet Safety recommends placing your cat’s carrier behind the front passenger seat or driver seat.
Crash tests have shown that the seatbelt used to secure a carrier can actually crush it in an accident.
Unless the manufacturer can show you that the carrier survives a crash test buckled up, don’t use the seat belts with your cat’s carrier.


















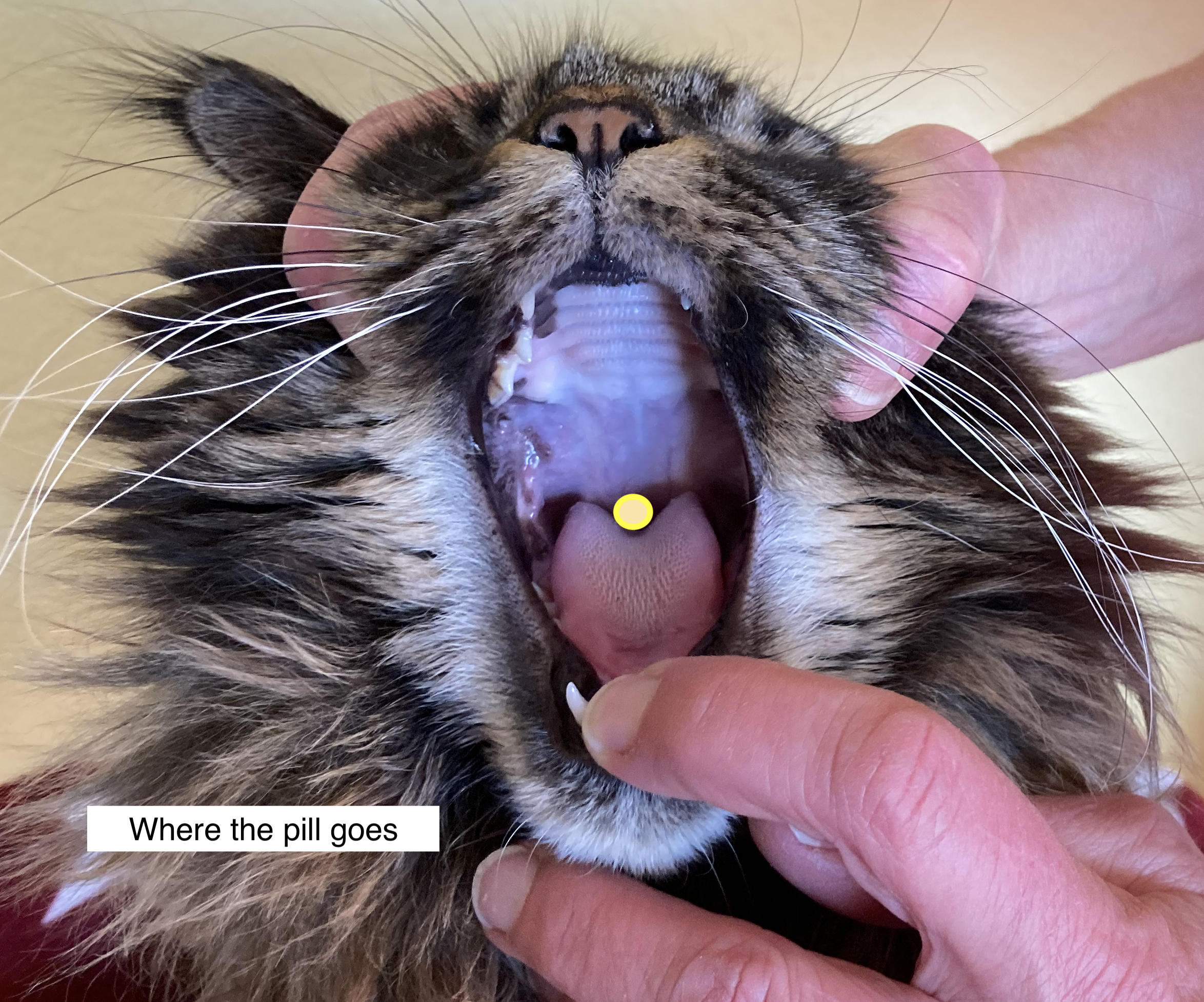

 Guide the Piller into the side of Kitty’s mouth
Guide the Piller into the side of Kitty’s mouth