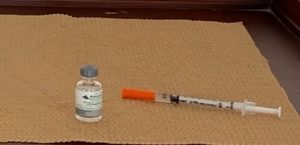
It is not uncommon for some cats to live completely indoors and have little contact with other animals. Do these cats really need rabies vaccines?
why Vaccinate your indoor cat for rabies
Rabies is one of the oldest diseases known to man – there are records of cases 4,000 years ago (Reference 1). Rabies is caused by a virus; infection with rabies results in a progressive inflammation of the brain and spinal cord. It is a disease of mammals – fish, reptiles and birds do not contract rabies nor do they carry rabies. Rabies is 100% fatal once clinical symptoms appear (Reference 2).
Rabies has two clinical forms (Reference 3):
- Furious: symptoms are hyperactivity, hallucinations, lack of coordination, fear of water and fear of fresh air. Death occurs after a few days due to cardio-respiratory arrest.
- Paralytic: Muscles become paralyzed starting at the wound site. Coma develops and eventually death occurs.
About 20% of rabies cases in humans are the paralytic form. Neither version of rabies is a pleasant way to die.
Rabies is estimated to cause at least 59,000 human deaths worldwide very year. In the US, only 1-3 cases are reported every year but 60,000 Americans get post-exposure treatment yearly after being bitten or scratched by a rabid animal (Reference 4).
Rabies – how is it transmitted?
Rabies is transmitted via the saliva of infected animals. Worldwide, 99% of cases result from bites of rabid dogs. (Reference 3)
In the U.S., 90% of reported cases in animals occur in wildlife, primarily raccoons, skunks, bats and foxes (Reference 4). Most human deaths in the U.S. from rabies (70%) are due to contact with infected bats (Reference 4).
A bat bite or scratch is very small and may be overlooked. Finding a bat in the house, particularly in a bedroom where someone was sleeping, warrants catching the bat and contacting your local health department for testing (Reference 5).
Rabies is diagnosed by detecting rabies virus antigens in brain tissue using a Direct Fluorescent Antibody (DFA) test. The animal must be euthanized to carry out this test (Reference 4).
rabies – treatment
Rabies is a disease that cannot be cured but can be prevented. After being bitten by a possibly rabid animal, a person must do the following to survive (Reference 4):
- wash the wound with soap and water
- receive a post-exposure rabies vaccine
- infiltrate the wound with rabies immunoglobulin or monoclonal antibodies if deemed necessary
why Vaccinate your indoor cat for rabies
In the U.S., most states or local health departments require that dogs and cats be vaccinated for rabies. The vaccine must be given by a licensed veterinarian. This ensures that the vaccine has been stored and administered properly and will be effective in the event your cat is bitten by a rabid animal. If the vaccine is not given by a veterinarian, the cat or dog is considered unvaccinated.
Dogs, cats and ferrets that are bitten by a potentially rabid animal and have never been vaccinated must be euthanized. Unlike humans, there is no post-exposure rabies vaccine for these animals (Reference 2). Vaccinated animals that have had exposure to rabies are re-vaccinated immediately and quarantined for at least 45 days.
If your cat bites someone, the physician treating the bite must notify the health Department. You must confine your cat for 10 days. If she is ill or becomes ill during the 10 day period, a veterinarian must evaluate her for rabies (Reference 2). This is another reason to vaccinate your indoor cat for rabies – proof of vaccination can forestall the health department from recommending euthanasia or quarantining your cat at a veterinary facility.
Vaccinate Your Indoor Cat for Rabies – Vaccines
There are two types of rabies vaccines recommended for cats in U.S. (Reference 6):
Inactivated:
- pathogen is unable to replicate in the host
- contains adjuvants and other proteins to promote immune response
- vaccines containing adjuvants cause more inflammation than vaccines without adjuvants
Recombinant:
- manipulation of the DNA of the pathogen reduces its virulence
- recombinant vaccines for cats in North America incorporate the pathogen DNA into the canarypox genome
- do not contain adjuvants
Kittens are typically vaccinated with their first rabies injection at 12-16 weeks of age. The next rabies vaccine is usually given at the 1 year anniversary of the initial vaccine; thereafter the owner has the option of annually vaccinating the cat or giving a vaccine approved for 3 years if this vaccine is accepted by local laws/regulations.
Side Effects of Vaccines
In a 2005 study (Reference 6), only 0.52% of cats had a reaction within 30 days of having a vaccine. These mild reactions included sleepiness, reduced appetite, mild fever or tenderness at the injection site.
More severe reactions are rare but can include vomiting, diarrhea, or facial swelling. Often these reactions can be mitigated by giving an antihistamine or steroid prior to vaccination (Reference 6).
Feline Injection Site Sarcomas (FISS) (Reference 6)
- malignant (cancerous) tumors recognized in the 1990’s
- these rapidly growing tumors occurred at the site where the vaccine was injected.
- FISS is estimated to occur in 1-4 cats per every 10,000 cats vaccinated
- Injections of vaccines and long-acting drugs have been associated with FISS
Rabies vaccines are typically given in the right hind leg below the knee. If an injection site tumor develops, the amputation of the leg offers a life-saving cure for the cat.
why vaccinate your indoor cat for rabies?
Even if your cat is 100% indoors, there is always a risk she may escape outdoors and encounter a rabid bat or raccoon. Alternatively, rabid bats and raccoons have been know to enter houses. Your cat may bite someone. If you decided not to vaccinate your indoor cat for rabies, you may be looking at euthanasia or an expensive quarantine at a veterinary facility.
If your cat is vaccinated, it protects not only her but you and your family, too. There is no cure for rabies, only prevention.
Rabies vaccines are safe for most cats. Your veterinarian is your best resource – discuss your cat’s vaccination needs and health history with him or her.
references
- Koury R, Warrington SJ. Rabies. [Updated 2022 Oct 31]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448076
- Animal and Rabies. Content source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of High-Consequence Pathogens and Pathology (DHCPP). January 26, 2022.https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/animals/index.html Viewed 4/24
- Jordan, J. Rabies. World Health Organization. https://www.who.int/health-topics/rabies#tab=tab_1 Viewed 4/24.
- Rabies in the U.S. Content source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of High-Consequence Pathogens and Pathology (DHCPP). April 6, 2020. https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/location/usa/index.html Viewed 4/24.
- Avoid Risk of Rabies from bats. Content source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Emerging and Zoonotic Infectious Diseases (NCEZID), Division of High-Consequence Pathogens and Pathology (DHCPP). https://www.cdc.gov/rabies/location/usa/index.html March 9, 2022. Viewed 4/24
- Stone AE, Brummet GO, Carozza EM, Kass PH, Petersen EP, Sykes J, Westman ME. 2020 AAHA/AAFP Feline Vaccination Guidelines. J Feline Med Surg. 2020 Sep;22(9):813-830. doi: 10.1177/1098612X20941784. PMID: 32845224.






 If you search for “monoclonal antibodies”, most of the search results are about COVID-19 and its variants. But did you know that monoclonal antibodies form the basis of the newest treatment for arthritis in cats? This new treatment is called
If you search for “monoclonal antibodies”, most of the search results are about COVID-19 and its variants. But did you know that monoclonal antibodies form the basis of the newest treatment for arthritis in cats? This new treatment is called  Many of us (cat owners) dread taking our cat to the vet. There is the ordeal of the carrier and car trip; once there, your cat seems miserable. However, regular veterinary care is the key to a happy and longer life for your cat. Can medication before your cat’s vet visit help?
Many of us (cat owners) dread taking our cat to the vet. There is the ordeal of the carrier and car trip; once there, your cat seems miserable. However, regular veterinary care is the key to a happy and longer life for your cat. Can medication before your cat’s vet visit help?
 Supplementation with fish oils has shown some benefit for arthritic cats.
Supplementation with fish oils has shown some benefit for arthritic cats.